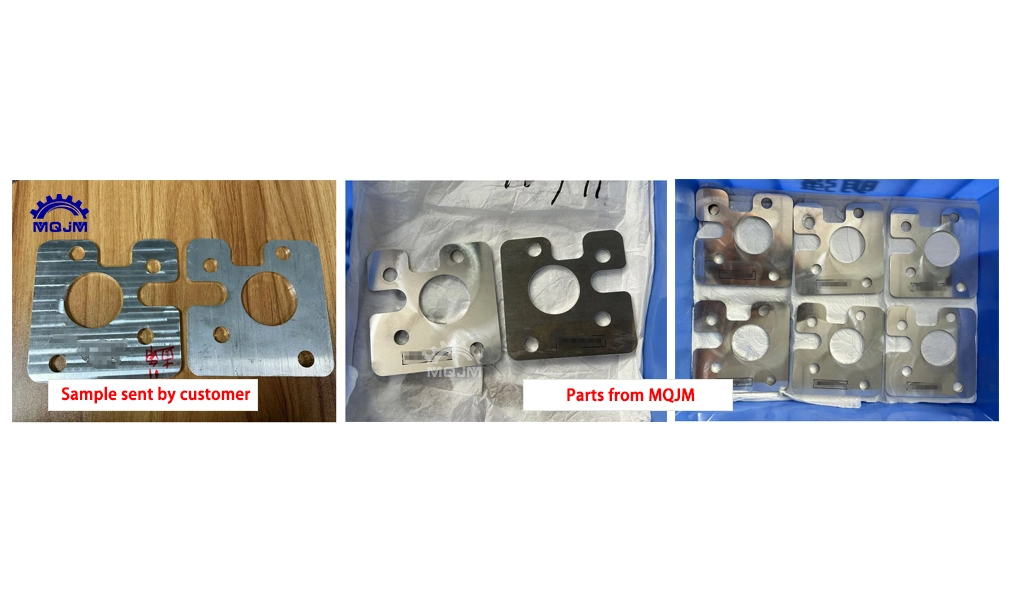
Stainless steel is widely used in industrial manufacturing due to its excellent corrosion resistance, strength and aesthetics. However, the surface of stainless steel parts may have roughness and unevenness after CNC milling processing, which requires appropriate surface treatment. In this paper, we will discuss the surface treatment methods of CNC milling stainless steel parts, mainly including the following four aspects.
Mechanical Grinding and Polishing
Mechanical grinding is a common preliminary surface treatment method after CNC milling. Through tools such as grinding wheels and sandpaper, burrs, knife marks and other defects on the surface of the parts are removed to improve the surface finish. Subsequently, tools such as polishing wheels and polishing creams can be used to polish the surface of the part to make it smoother and brighter. This method is suitable for parts with high requirements for surface finish.
Chemical Treatment
Chemical treatment is the use of chemical reactions to improve the performance of the surface of CNC milling stainless steel parts. Common chemical treatment methods include pickling, passivation and so on. Pickling can remove the surface of the parts of the oxide skin, rust and other impurities, to improve the cleanliness of the surface. Passivation, on the other hand, is to form a dense oxide film on the surface of the part through a chemical reaction to improve the corrosion resistance of the part. After chemical treatment, the surface of CNC milling stainless steel parts is flat, smooth, and has good corrosion resistance.
Electrochemical Treatment
Electrochemical treatment is the use of electrochemical principles on the surface of CNC milling stainless steel parts processing methods. Among them, electroplating is one of the most common electrochemical treatment methods. By plating a layer of metal or alloy on the surface of the parts, the surface properties of the parts can be improved, such as improving wear resistance and corrosion resistance. In addition, electrolytic polishing is also a commonly used electrochemical treatment method, which can make the surface of CNC milling stainless steel parts reach a very high degree of finish in a short time.
Surface Coating Technology
Surface coating technology is to apply one or more layers of coating on the surface of CNC milling stainless steel parts to improve the surface properties of the parts. Common coating materials include paints, coatings, plastics and so on. The coating can protect the surface of the parts from corrosion, abrasion and other damage, and improve the service life of the parts. In addition, some special function coatings can also give the parts special properties, such as anti-static, anti-radiation and so on. When choosing coating materials, you need to make a reasonable choice according to the use environment and requirements of the parts.
Through the above four surface treatment methods, the surface performance of CNC milling stainless steel parts can be effectively improved, and the quality and reliability of the parts can be improved. In practical application, the appropriate surface treatment method can be selected according to the specific requirements of the parts to obtain the best treatment effect.