The CNC machine programming process involves converting the geometric information and technical requirements from design drawings into G-code that the machine can execute. This process relies on CAD and CAM software to ultimately generate the CNC code. Today, MQJM will guide you through the detailed steps:
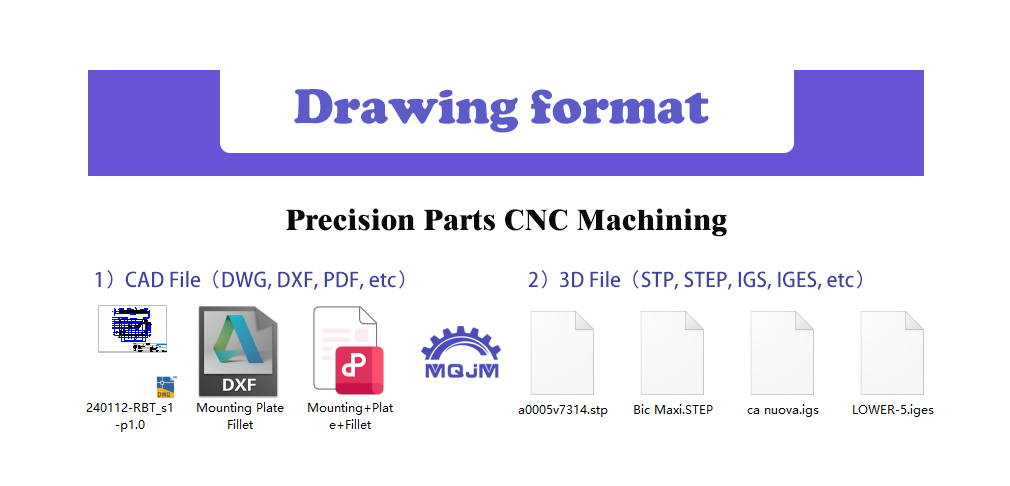
First, prepare and import 2D drawings (such as DWG, DXF, or PDF formats) or 3D models (such as STEP or IGES formats), analyzing the geometric shapes, machining tolerances, materials, and surface treatment requirements on the drawings. Next, import the drawings or models into CAM software (such as Mastercam or Fusion 360) and set the workpiece’s coordinate system and machining starting point.
Then, select the tools (such as drills or end mills) and materials based on the type of machine, and set the tool parameters. Next, define the machining strategy, which includes rough machining, finishing, and drilling steps. Generate the toolpath and simulate the machining process using CAM software to check the path's rationality and avoid collisions.
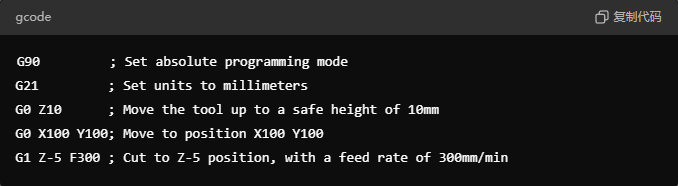
Once confirmed, generate the G-code file and upload it to the CNC machine via USB or network. Finally, fix the workpiece on the machine, calibrate the tool position, and start the program for automatic machining. After machining is complete, use measuring tools to inspect the part's quality and ensure it meets design specifications.












